Automatic Foot Ulcer Segmentation Using an Ensemble of Convolutional Neural Networks
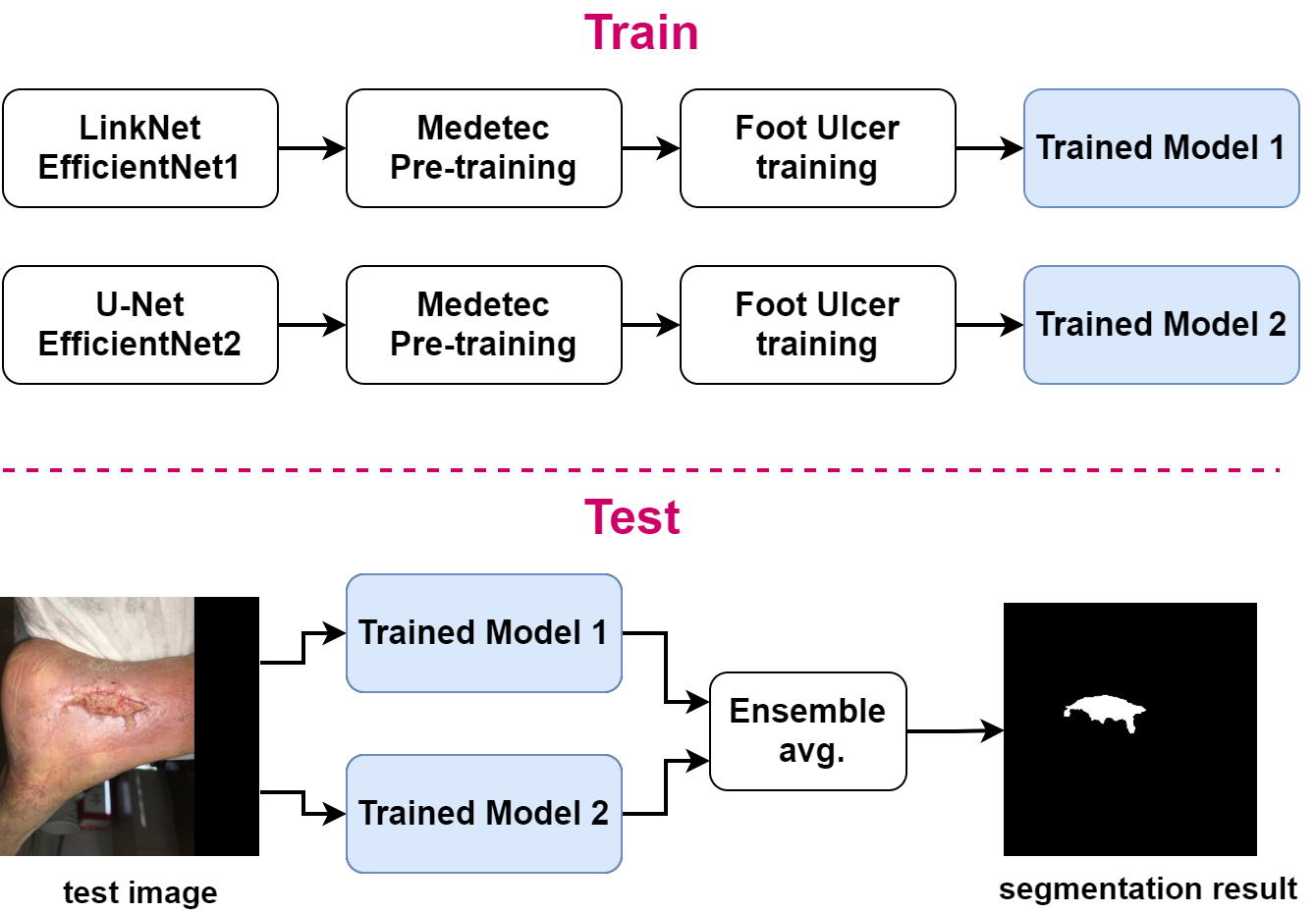
Foot ulcer is a common complication of diabetes mellitus and, associated with substantial morbidity and mortality, remains a major risk factor for lower leg amputations. Extracting accurate morphological features from foot wounds is crucial for appropriate treatment. Although visual inspection by a medical professional is the common approach for diagnosis, this is subjective and error-prone, and computer-aided approaches thus provide an interesting alternative. Deep learning-based methods, and in particular convolutional neural networks (CNNs), have shown excellent performance for various tasks in medical image analysis including medical image segmentation. In this paper, we propose an ensemble approach based on two encoder-decoder-based CNN models, namely LinkNet and U-Net, to perform foot ulcer segmentation. To deal with a limited number of available training samples, we use pre-trained weights (EfficientNetB1 for the LinkNet model and EfficientNetB2 for the U-Net model) and perform further pre-training using the Medetec dataset while also applying a number of morphological-based and colour-based augmentation techniques. To boost the segmentation performance, we incorporate five-fold cross-validation, test time augmentation and result fusion. Applied on the publicly available chronic wound dataset and the MICCAI 2021 Foot Ulcer Segmentation (FUSeg) Challenge, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance with data-based Dice scores of 92.07% and 88.80%, respectively, and is the top ranked method in the FUSeg challenge leaderboard. The Dockerised guidelines, inference codes and saved trained models are publicly available at https://github.com/masih4/Foot_Ulcer_Segmentation.
PDF Abstract