Search Results for author: Guanglei Zhang
Found 9 papers, 8 papers with code
Generating Progressive Images from Pathological Transitions via Diffusion Model
2 code implementations • 21 Nov 2023 • Zeyu Liu, Tianyi Zhang, Yufang He, Yunlu Feng, Yu Zhao, Guanglei Zhang
Deep learning is widely applied in computer-aided pathological diagnosis, which alleviates the pathologist workload and provide timely clinical analysis.
PuzzleTuning: Explicitly Bridge Pathological and Natural Image with Puzzles
1 code implementation • 12 Nov 2023 • Tianyi Zhang, Shangqing Lyu, Yanli Lei, Sicheng Chen, Nan Ying, Yufang He, Yu Zhao, Yunlu Feng, Hwee Kuan Lee, Guanglei Zhang
Pathological image analysis is a crucial field in computer vision.
CPIA Dataset: A Comprehensive Pathological Image Analysis Dataset for Self-supervised Learning Pre-training
1 code implementation • 27 Oct 2023 • Nan Ying, Yanli Lei, Tianyi Zhang, Shangqing Lyu, Chunhui Li, Sicheng Chen, Zeyu Liu, Yu Zhao, Guanglei Zhang
This paper presents the comprehensive pathological image analysis (CPIA) dataset, a large-scale SSL pre-training dataset combining 103 open-source datasets with extensive standardization.
CellMix: A General Instance Relationship based Method for Data Augmentation Towards Pathology Image Classification
1 code implementation • 27 Jan 2023 • Tianyi Zhang, Zhiling Yan, Chunhui Li, Nan Ying, Yanli Lei, Yunlu Feng, Yu Zhao, Guanglei Zhang
In pathology image analysis, obtaining and maintaining high-quality annotated samples is an extremely labor-intensive task.
Shuffle Instances-based Vision Transformer for Pancreatic Cancer ROSE Image Classification
1 code implementation • 14 Aug 2022 • Tianyi Zhang, Youdan Feng, Yunlu Feng, Yu Zhao, Yanli Lei, Nan Ying, Zhiling Yan, Yufang He, Guanglei Zhang
The rapid on-site evaluation (ROSE) technique can signifi-cantly accelerate the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer by im-mediately analyzing the fast-stained cytopathological images.
Pancreatic Cancer ROSE Image Classification Based on Multiple Instance Learning with Shuffle Instances
no code implementations • 7 Jun 2022 • Tianyi Zhang, Youdan Feng, Yunlu Feng, Guanglei Zhang
Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) using the deep learning method has the potential to solve the problem of insufficient pathology staffing.
MSHT: Multi-stage Hybrid Transformer for the ROSE Image Analysis of Pancreatic Cancer
1 code implementation • 27 Dec 2021 • Tianyi Zhang, Yunlu Feng, Yu Zhao, Guangda Fan, Aiming Yang, Shangqin Lyu, Peng Zhang, Fan Song, Chenbin Ma, Yangyang Sun, Youdan Feng, Guanglei Zhang
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most malignant cancers in the world, which deteriorates rapidly with very high mortality.
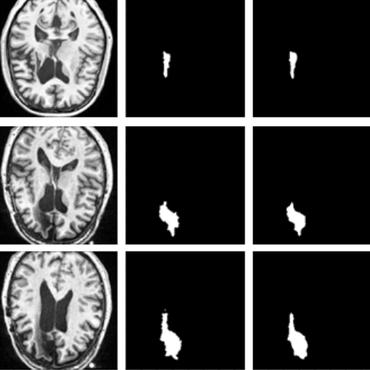
Prior Attention Network for Multi-Lesion Segmentation in Medical Images
1 code implementation • 10 Oct 2021 • Xiangyu Zhao, Peng Zhang, Fan Song, Chenbin Ma, Guangda Fan, Yangyang Sun, Youdan Feng, Guanglei Zhang
The proposed network can be regarded as a universal solution to multi-lesion segmentation in both 2D and 3D tasks.
D2A U-Net: Automatic Segmentation of COVID-19 Lesions from CT Slices with Dilated Convolution and Dual Attention Mechanism
1 code implementation • 10 Feb 2021 • Xiangyu Zhao, Peng Zhang, Fan Song, Guangda Fan, Yangyang Sun, Yujia Wang, Zheyuan Tian, Luqi Zhang, Guanglei Zhang
In this paper we propose a dilated dual attention U-Net (D2A U-Net) for COVID-19 lesion segmentation in CT slices based on dilated convolution and a novel dual attention mechanism to address the issues above.